How to use database via SQL. There are several options. For example, you can connect the database in parallel, using ODBC, via SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, etc.
Example 1:
Simple, with an existing table:
4 steps:
1 – Script . Place the script, for example, in the OnAfterUpdate event .
2 – DSN . Define the DSN in the script.
3 – Table . Define the already existing table, in the script.
4 – Tags . Define which tags in the script.
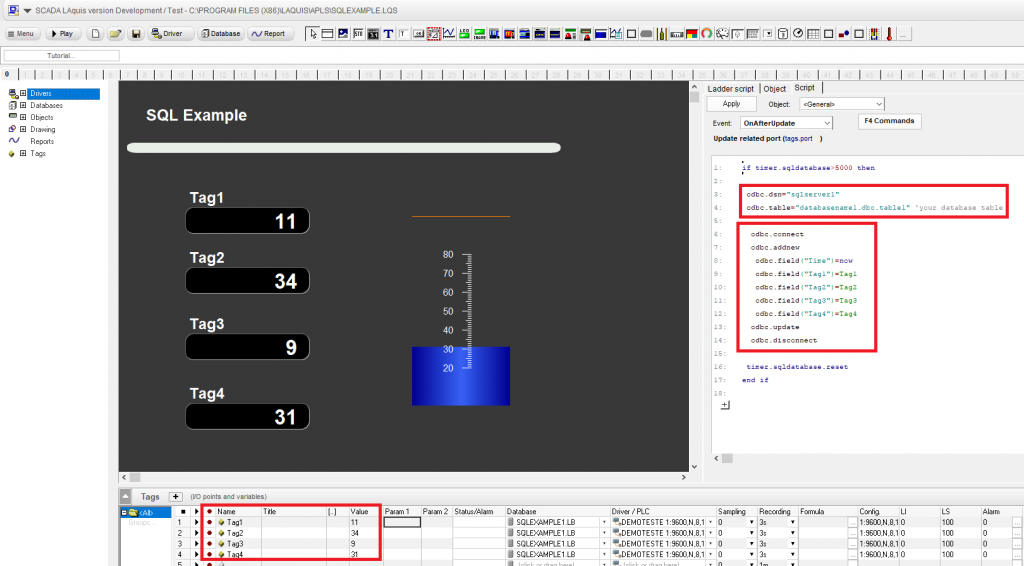
Script :
Event OnAfterUpdate
if timer.sqldatabase>5000 then 'set timeline (ms) odbc.dsn="sqlserver1" 'set DSN odbc.table="databasename1.dbo.table1" 'set table odbc.connect odbc.addnew odbc.field("Time")=now ' set TAGS: odbc.field("Tag1")=Tag1 odbc.field("Tag2")=Tag2 odbc.field("Tag3")=Tag3 odbc.field("Tag4")=Tag4 odbc.update odbc.disconnect timer.sqldatabase.reset end if
Example 2
Automatically all tags, with already existing table.
Script :
if timer.sqldatabase>5000 then 'set timeline (ms) odbc.dsn="sqlserver1" 'set DSN odbc.table="databasename1.dbo.table" 'set table odbc.connect odbc.addnew odbc.field("Time")=now for i=1 to tags.count odbc.field(tag$(i).name)=tag(i) next odbc.update odbc.disconnect timer.sqldatabase.reset end if
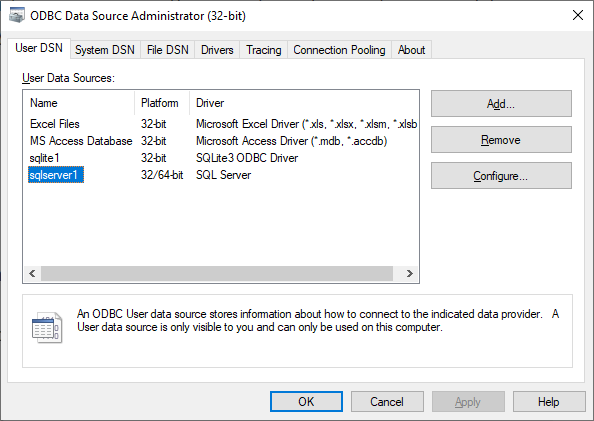
* DSN:
The DSN can be defined in the Windows ODBC command.
Example 3:
SELECT fields example from SQL database:
Script :
odbc.dsn="sqlserver1" 'set DSN odbc.connect odbc.SQLExecute("SELECT * FROM databasename1.dbo.table1" ) 'set query odbc.moveLast n = odbc.recordCount s = "" s = odbc.field("Tag1") ' read field msgBox(s) odbc.disconnect